Encor Mouse Monoclonal to Anti-Arrestin-1 / S-antigen
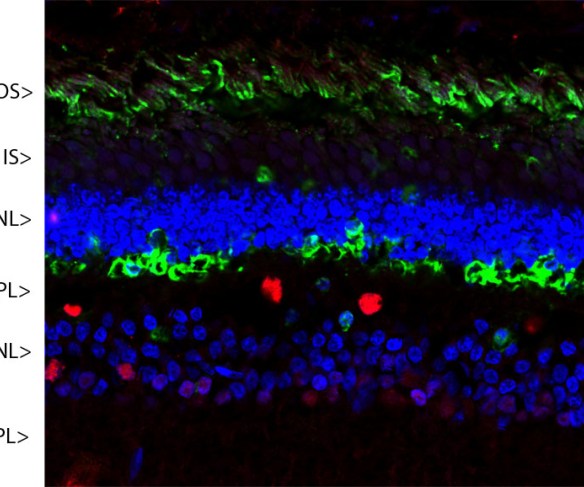
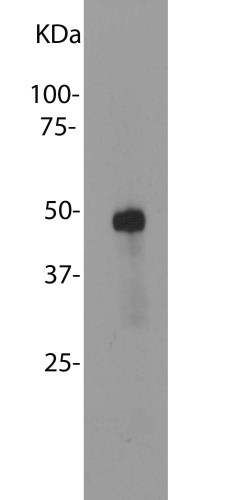
The arrestin proteins are a family of regulators of cell signaling of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). Visual arrestin was first discovered as a result of the experimental model of human uveitis, an autoimmune disease of the eye. In this model, called experimental allergic uveitis, animals were injected with extracts made from the retina of the same species mixed with Freund’s complete adjuvant. The animals mounted a strong immune response to the extract, and the antibody response was used to identify several immunogenic retinal proteins. One of these was called S-antigen, for soluble antigen. The protein was found to be abundant in retina, about 48 kDa in molecular weight, and localized in the outer segments of the photoreceptors (1, 2).
Several years later, Hermann Kühn and colleagues discovered that this protein binds to phosphorylated rhodopsin and prevents this protein from activating transducin (3, 4, 5). Transducin is a typical heterotrimeric G protein, composed of α and βγ subunits. Rhodopsin phosphorylation is mediated by Rhodopsin kinase (a.k.a. GRK1), the prototypic member of a family of GPCR kinases. Since the S-antigen protein arrested the activity of rhodopsin it was renamed arrestin, and became the prototypic member of the arrestin protein family.
Subsequently, Robert Lefkowitz and colleagues discovered a related protein which bound to phosphorylated β-adrenergic GPCRs and prevented these proteins from activating their specific heterotrimeric G proteins (6). Because of this relationship to the β-adrenergic receptor and functional and structural similarities to visual arrestin this protein was named β-arrestin. The β-adrenergic receptor was phosphorylated by the β-adrenergic receptor kinase (a.k.a. GRK2), an enzyme belonging to GPCR kinase family.
Studies of visual transduction therefore aided greatly in understanding other kinds of GPCR signaling. In mammals, there are four arrestin isoforms, Visual arrestin (a.k.a. S-antigen and arrestin-1) and cone arrestin (a.k.a. arrestin-4) are largely confined to photoreceptors. β-arrestin 1 (a.k.a. arrestin 2) and β-arrestin-2 (a.k.a. arrestin-3) are ubiquitous and regulate non-visual GPCRs.
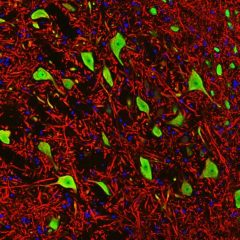
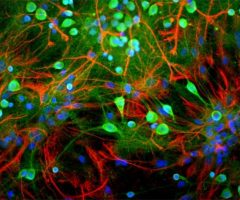
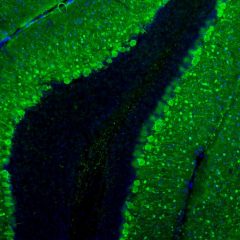
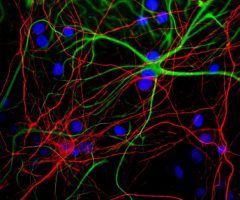
MCA-S128 was raised against recombinant bovine arrestin-1 with the first 20 amino acids of the C-terminus truncated. The antibody does not bind the other three arrestin molecules. In the retina, MCA-S128 binds to rod cell bodies and rod outer segments. The HGNC name for this protein is SAG.
HGNC name(s) : SAG
Host : Mouse
Clonality : Monoclonal
ID : EnCor Biotechnology Arrestin-1 / S-antigen S128
Reactivity : Human | Horse | Cow | Pig | Chicken | Rat | Mouse
Isotype : IgG1
Conjugation : none
Immunogen : Recombinant bovine with the first20 C-term aa truncated
Mass of detected protein : 48 kDa
Uniprot ID : P10523
KGNC name : SAG
RRID # : AB_2572227
Purification : Affinity purified at 1 mg/mL
Storage : Shipped on ice. Store at 4°C. For long term storage, leave frozen at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Validated applications : WB | IF/ICC | IHC
Suggested Dilutions:
WB: 1:5 000
IF/IHC: 1:1 000
References :
1. Dorey C, Faure JP. [Isolation and characterization of a retinal antigen inducing experimental autoimmune uveo-retinitis]. [Article in French] Ann Immunol (Paris). 128:229-32 (1977).
2. Wacker WB, Donoso LA, Kalsow CM, Yankeelov JA Jr, Organisciak DT. Experimental allergic uveitis. Isolation, characterization, and localization of a soluble uveitopathogenic antigen from bovine retina. J Immunol. 119:1949-58 (1977).
3. Kühn H, Hall SW, Wilden U. Light-induced binding of 48-kDa protein to photoreceptor membranes is highly enhanced by phosphorylation of rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 176:473-8 (1984).
4. Pfister C, Chabre M, Plouet J, Tuyen VV, De Kozak Y, Faure JP, Kühn H. Retinal S antigen identified as the 48K protein regulating light-dependent phosphodiesterase in rods. Science 228:891-3 (1985).
5. Wilden U, Hall SW, Kühn H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1174-8 (1986).
6. Lohse MJ, Benovic JL, Codina J, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. β-arrestin: a protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science 248: 1547-1550 (1990).
7. Smith WC, Mc Dowell JH, Dugger DR, Miller R, Arendt A, Popp MP, Hargrave PA. Identification of regions of arrestin that bind to rhodopsin. Biochemistry 38:2752-61 (1999).
Additional information
| Format | 50 ul, 100 ul, 500 ul |
|---|---|
| Supplier | |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Conjugation | None |

Reviews