Encor Mouse Monoclonal to Ubiquilin 2, UBQLN2
Ubiquilin 2, also known as PLIC2 and Chap1, is a member of the ubiquilin protein family, which regulate the degradation of cellular proteins through proteasome or autophage-like pathways (1, 2, 3). Humans have four ubiquilin genes, each encoding a separate protein referred to as Ubiquilin 1, 2, 3 and 4. All ubiquilins contain an N-terminal ubiquitin-like (UBL) domain and a C-terminal ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain, while the central part of the molecules are highly variable. The UBL domains bind subunits of the proteasome, and the UBA domains binds to polyubiquitin chains that are typically conjugated onto proteins marked for proteosomal degradation (1).
Ubiquilin 2 has a unique region close to the C terminus containing 12 PXX tandem collagen like repeats, where P is proline and X is most cases valine, glycine, isoleucine or threonine. Teepu Siddique and his collaborators have identified mutations in the ubiquilin 2 gene leading to protein point mutations which were important contributors to several forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). Interestingly, these mutations involved alterations in proline residues in the PXX repeat region (P497H, P497S, P506T, P509S and P525S, ref. 4).
Recently, the Lee and Trojanowski group investigated C9orf72 hexanucleotide expansion and ubiquilin 2 pathology in patients with ALS and FTLD by genetic analysis and immunohistochemistry and found distinct ubiquilin 2 pathology in ALS and FTLD-TDP with C9orf72 expansion (5). C9orf72 hexonucleotide expansion is the most common cause to date of familial ALS and FTLD (6, 7).
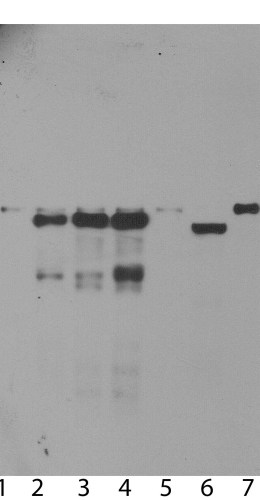
Ubiquilin 2 protein is of different molecular size in mouse and human, 638 and 624 amino acids, respectively. As a result the mouse protein, endogenously expressed in rodent 3T3 cells, runs on SDS-PAGE and western blots slightly slower than the human protein.
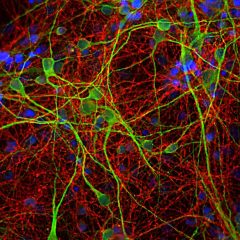
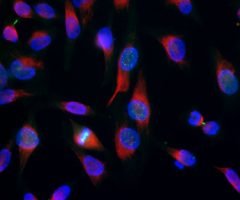
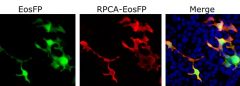
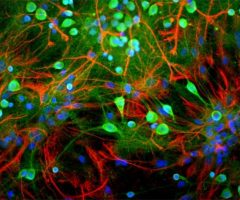
Our antibody MCA-6H9 was raised against human ubiquilin 2 expressed in and purified from E. coli. The HGNC name for this protein is UBQLN2.
HGNC name(s) : UBQLN2
Host : Mouse
Clonality : Monoclonal
ID : EnCor Biotechnology Ubiquilin 2 6H9
Reactivity : Human | Horse | Cow | Pig | Chicken | Rat | Mouse
Isotype : IgG1
Conjugation : none
Immunogen : Recombinant full length human
Mass of detected protein : 66-68 kDa
Uniprot ID : Q9UHD9
KGNC name : UBQLN2
RRID # : AB_2572390
Purification : Affinity purified at 1 mg/mL
Storage : Shipped on ice. Store at 4°C. For long term storage, leave frozen at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
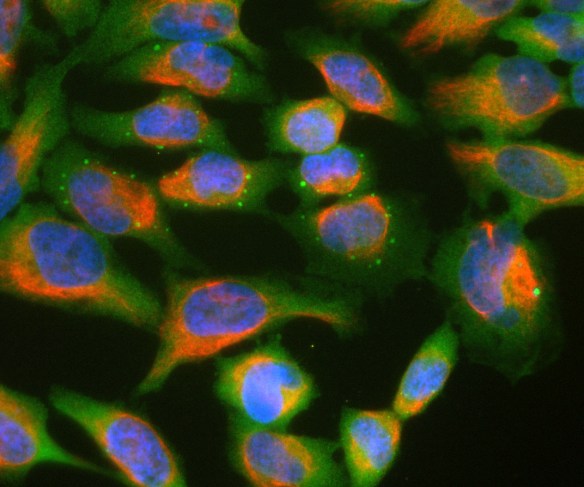
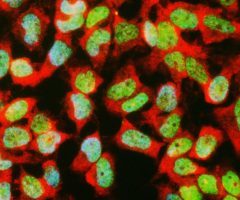
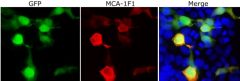
Validated applications : WB | IF/ICC | IHC
Suggested Dilutions:
WB: 1:1 000-1:2 000. ICC/IF and IHC: 1:1 000.
References :
1. Kleijnen MF, Shih AH, Zhou P, Kumar S, Soccio R E, Kedersha N L, Gill G, Howley PM. The hPLIC proteins may provide a link between the ubiquitination machinery and the proteasome. Molec. Cell 6: 409-419 (2000).
2. N’Diaye EN, Kajihara KK, Hsieh I, Morisaki H, Debnath J, Brown EJ. PLIC proteins or ubiquilins regulate autophagy-dependent cell survival during nutrient starvation. EMBO Rep. 10:173-9 (2009).
3. Rothenberg C, Srinivasan D, Mah L, Kaushik S, Peterhoff CM, Ugolino J, Fang S, Cuervo AM, Nixon RA, Monteiro MJ. Ubiquilin functions in autophagy and is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Hum Mol Genet. Aug 15,19 (16): 3219-32. Epub Jun 7 (2010).
4. Deng HX, Chen W, Hong ST, Boycott KM, Gorrie GH, Siddique N, Yang Y, Fecto F, Shi Y, Zhai H, Jiang H, Hirano M, Rampersaud E, Jansen GH, Donkervoort S, Bigio EH, Brooks BR, AjroudK, Sufit RL, Haines JL, Mugnaini E, Pericak-Vance MA, Siddique T. Mutations in UBQLN2 cause dominant X-linked juvenile and adult-onset ALS and ALS/dementia. Nature Aug 21,477(7363):211-5 (2011).
5. Brettschneider J, Van Deerlin VM, Robinson JL, Kwong L, Lee EB, Ali YO, Safren N, Monteiro MJ, Toledo JB, Elman L, McCluskey L, Irwin DJ, Grossman M, Molina-Porcel L, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Pattern of ubiquilin pathology in ALS and FTLD indicates presence of c9orf72 hexanucleotide expansion. Acta Neuropathol. Jun,123 (6):825-39 (2012).
6. Renton AE, Majounie E, Waite AA, et al. Hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD. Neuron. Oct 20,72(2):257-68 (2011).
7. DeJesus-Hernandez M, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF, Boxer AL, Baker M, Rutherford NJ, Nicholson AM, Finch NA, Flynn H, Adamson J, Kouri N, Wojtas A, Sengdy P, Hsiung GY, Karydas A, Seeley WW, Josephs KA, Coppola G, Geschwind DH, Wszolek ZK, Feldman H, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Miller BL, Dickson DW, Boylan KB, Graff-Radford NR, Rademakers R. Expanded GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in noncoding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked FTD and ALS. Neuron.Oct 20,72(2):245-56 (2011).
Additional information
| Format | 50 ul, 100 ul, 500 ul |
|---|---|
| Supplier | |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Conjugation | None |

Reviews