Encor Mouse monoclonal to Parvalbumin
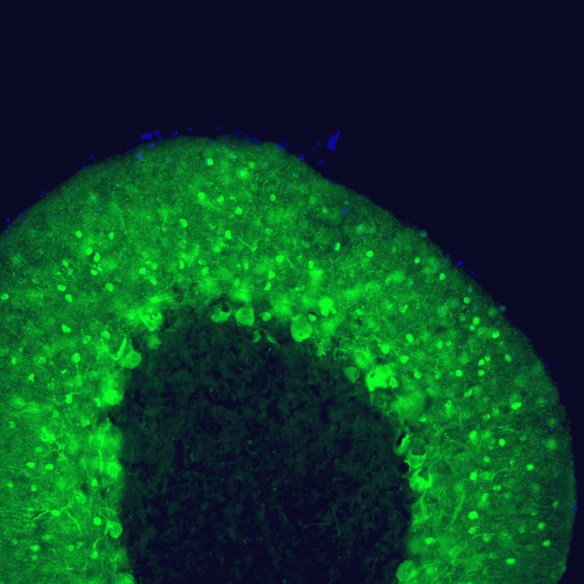
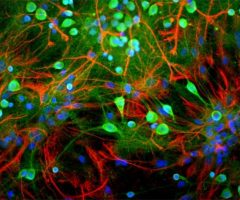
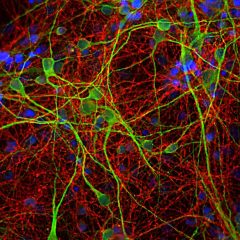
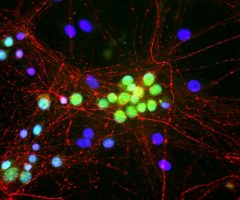
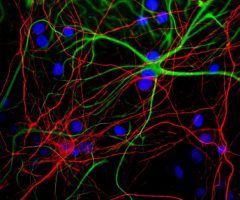
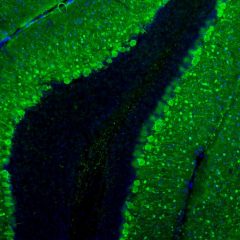
Parvalbumin is a cytoplasmic low molecular weight Ca2+ binding proteins with. It is the prototypic member of the very large family of proteins containing the “EF hand” Ca2+ binding motif (1). The nomenclature comes from the parvalbumin structure in which the fifth and sixth alpha helices, the E and F helices, form a V shape including acid amino acids which co-ordinate a single Ca2+. It turns out that close variants of this structure are found in many other Ca2+ binding proteins. Parvalbumin is expressed in fast-contracting muscles, where its levels are highest, as well as in the brain and some endocrine tissues. In brain, it is particularly concentrated in Purkinje cells and interneurons in the molecular layer of the cerebellum, but is also found in many GABAergic interneurons in the cortex. These GABAergic interneurons in most cases express only one of three Ca2+ binding proteins, namely parvalbumin, calretinin, or calbindin. As a result, these important inhibitory interneurons can be identified and subclassified based on their content of these three proteins (2). Each type of neuron as defined in this fashion has particular electrophysiological and functional properties. For example, calbindin positive interneurons are not fast-spiking as are parvalbumin expressing interneurons.
Parvalbumin contains 3 EF-hand domains, domain AB, CD and EF. The N-terminal EF-hand of parvalbumin does not bind Ca2+, so that functional Ca2+ binding is between helices C and D and between helices E and F. The function of parvalbumin appears to be primarily buffering the Ca2+ level in cells. Absence of parvalbumin and calbindin disrupts the regulation of Purkinje cell firing rate and rhythmicity in vivo and parvalbumin dysfunction in cells critically contributes to abnormalities in oscillatory rhythms and network (3, 4). The HGNC name for this protein is PVALB.
HGNC name(s) : PVALB
Host : Mouse
Clonality : Monoclonal
ID : EnCor Biotechnology Parvalbumin 3C9
Reactivity : Human | Rat | Mouse | Cow
Isotype : IgG1
Conjugation : none
Immunogen : Recombinant full length human
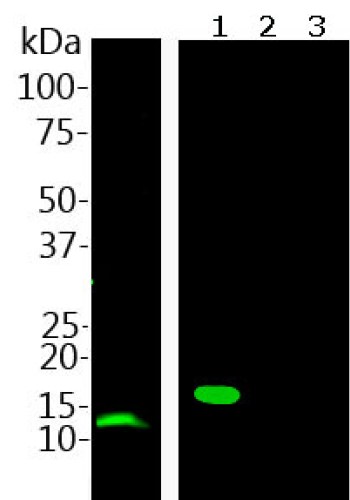
Mass of detected protein : 12 kDa
Uniprot ID : P20472
KGNC name : PVALB
RRID # : AB_2572372
Purification : Affinity purified at 1 mg/mL
Storage : Shipped on ice. Store at 4°C. For long term storage, leave frozen at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Validated applications : WB | IF/ICC | IHC
Suggested Dilutions:
WB: 1:1 000-1:5 000
ICC/IF or IHC: 1:1 000-1:5 000
References :
1: Kretsinger RH, Nockolds CE. Carp Muscle Calcium-binding Protein: II. Structure determination and general description. J. Biol. Chem. 248:3313-3326 (1973).
2: Andressen C, Bliimcke I, Celio MR. Calcium-binding proteins: selective markers of nerve cells. Cell Tissue Res 271:181-208 (1993).
3: Bearzatto B, Schwaller B, Dumont M, De Saedeleer C, Dan B, Barski JJ, Schiffmann SN, Cheron G. Mono- and dual-frequency fast cerebellar oscillation in mice lacking parvalbumin and/or calbindin D-28k. Eur J Neurosci.22(4):861-70 (2005)
4: Schwaller B, Meyer M, Schiffmann S. ‘New’ functions for ‘old’ proteins: The role of the calcium binding proteins calbindin D-28k, calretinin and parvalbumin, in cerebellar physiology. Studies with knockout mice. The Cerebellum 1:241–258 (2002).
Additional information
| Format | 50 ul, 100 ul, 500 ul |
|---|---|
| Supplier | |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Conjugation | None |

Reviews