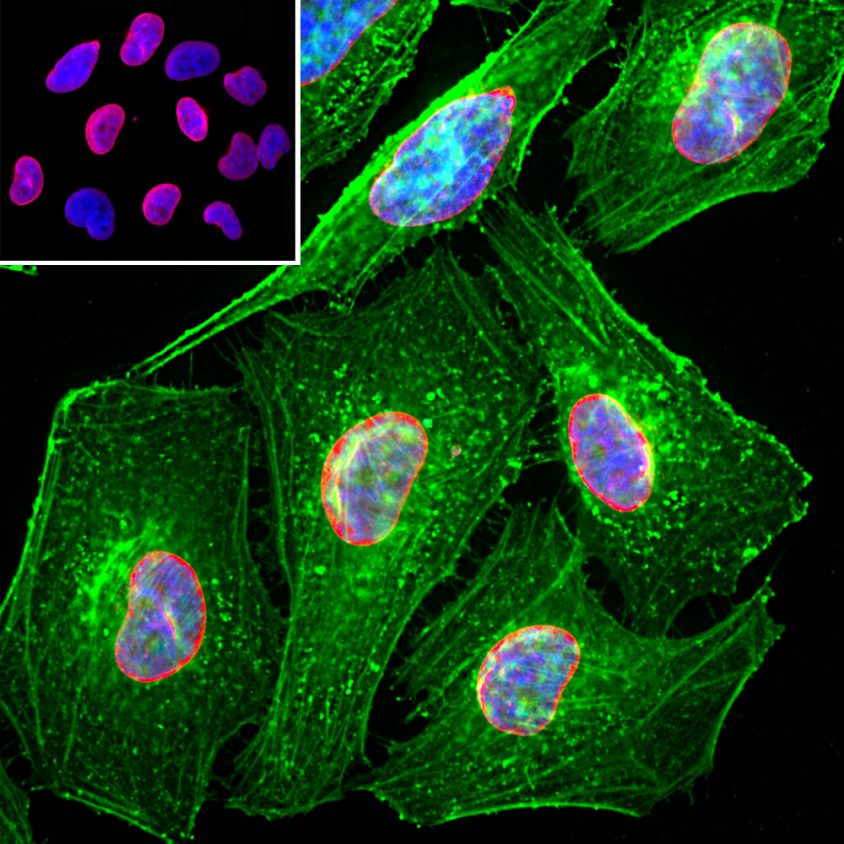
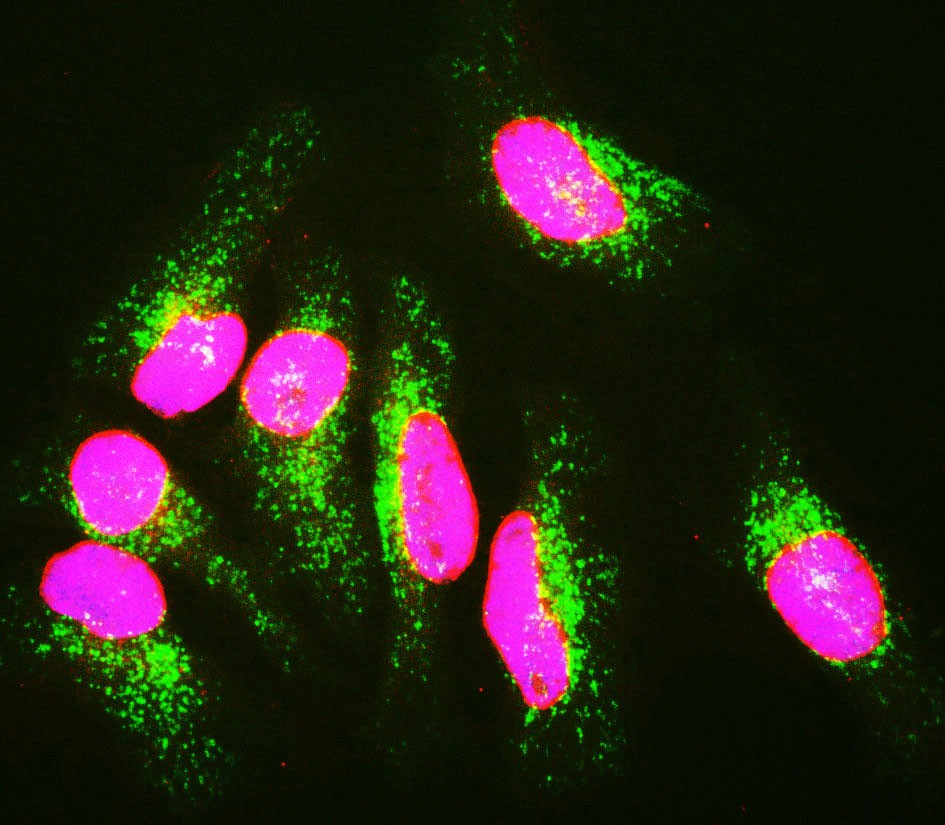
Encor Chicken Polyclonal to Lamin A/C
The Lamin proteins are members of the intermediate filament protein family but are located inside the nucleus rather than in the cytoplasm (1). The lamins function as skeletal components tightly associated with the inner nuclear membrane.
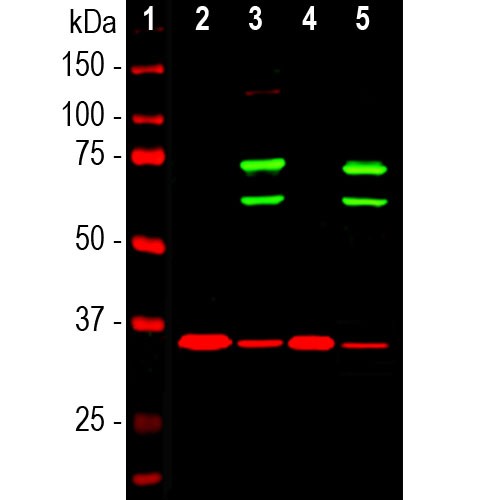
Originally the proteins of the nuclear cytoskeleton were named Lamin A, B and C, from top to bottom as visualized on SDS-PAGE gels. Subsequently, it was found that Lamins A and C were coded for by a single gene (2), while the Lamin B band may contain two proteins encoded by two genes now called Lamin B1 and Lamin B2. Lamin A has a mass of about 74 kDa while Lamin C is 65 kDa. The Lamin A protein includes a C-terminal segment of 98 amino acids missing from Lamin C, while Lamin C has a unique C-terminal 6 amino acid peptide not present in Lamin A. Apart from these regions Lamin A and C are identical so that antibodies raised against either protein are likely to cross react with the other.
This is the case with this polyclonal, which was raised against full length recombinant human Lamin A. Lamin polymerization and depolymerization is regulated by phosphorylation by cyclin dependent protein kinase 1 (CDK1), the key component of “maturation promoting factor“, the central regulator of cell division. Activity of this kinase increases during cell division and is responsible for the breakdown of the nuclear lamina.
Mutations in the LMNA gene are associated with several serious human diseases, including Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, familial partial lipodystrophy, limb girdle muscular dystrophy, dilated cardiomyopathy, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2B1, and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. This family of diseases belong to a larger group which are often referred to as Laminopathies, though some laminopathies are associated in defects in Lamin B1, B2 or one or other of the numerous nuclear lamina binding proteins. A truncated version of lamin A, commonly known as progerin, causes Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, a form of premature aging (3). The HGNC name for this protein is LMNA.
HGNC name(s) : LMNA
Host : Chicken
Clonality : Polyclonal
ID : EnCor Biotechnology Lamin A/C LaminAC
Reactivity : Human | Horse | Cow | Pig | Chicken | Rat | Mouse
Isotype : IgY
Conjugation : none
Immunogen : Recombinant full length human
Mass of detected protein : 65 and 74 kDa
Uniprot ID : P02545
KGNC name : LMNA
RRID # : AB_2572338
Purification : Concentrated IgY preparation
Storage : Shipped on ice. Store at 4°C. For long term storage, leave frozen at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
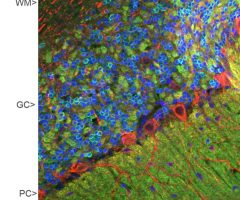
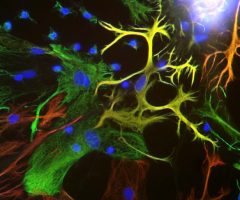
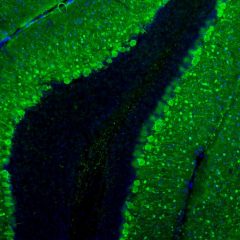
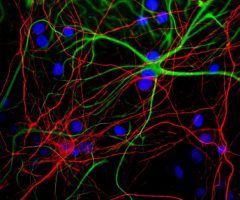
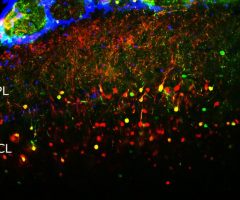
Validated applications : WB | IF/ICC | IHC
Suggested Dilutions:
WB: 1:2 000. IF/ICC and IHC: 1:1 000 .
References :
1. Fisher, D. Z., Chaudhary, N., Blobel, G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 83: 6450-6454 (1986).
2. McKeon, F. D., Kirschner, M. W., Caput, D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature 319: 463-468 (1986).
3. Liu, B. and Zhou, Z. Lamin A/C, laminopathies and premature ageing. Histol. Histopathol. 23: 747-763 (2006).
Additional information
| Format | 50 ul, 100 ul, 500 ul |
|---|---|
| Supplier | |
| Host | Chicken |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Reactivity | Chicken, Cow, Horse, Human, Mouse, Pig, Rat |
| Validated Applications | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Conjugation | None |
| Isotype | IgY |


Reviews