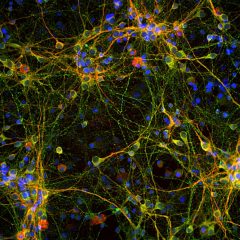
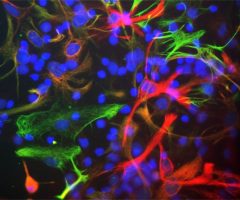
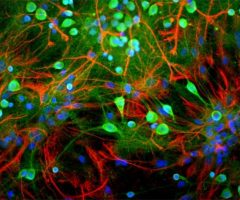
Encor Mouse monoclonal antibody against C3
Complement component 3, often simply called C3, is the third protein in the complement system. The complement system is a part of the immune system to “complement” the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens such as bacteria and viruses from the organism, trigger inflammation and remove debris from cells and tissues (1). C3 plays a central role in complement activation, and is involved in both the classical and alternative pathway. C3 is synthesized as an intracellular precursor (pro-C3) of 185 kDa which is processed by proteolytic cleavage into two large chains called the α subunit (115 kDa) and the β sunbunit (70 kDa) which are however linked by a disulfide bond (2).
C3 activation involves further cleavage by C3 convertase to produce C3a (9 kDa) and C3b (the remaining 176 kDa of the β subunit and truncated α subunits). C3a is released into the surrounding fluids and can bind to receptors on basophils and mast cells triggering them to release their vasoactive contents (e.g., histamine). Because of the role of these materials in anaphylaxis, C3a is called an anaphylatoxin, and the N-terminal region of the α subunit is referred to as the anaphyloxin domain. In blood, C3a may be further cleaved by carboxypeptidase to produce C3adesArg or ASP (acylation-stimulating protein), which acts as a paracrine signal to increase triglyceride synthesis in adipocytes (3). C3adesArg have been demonstrated to be present at increased levels in patients with obesity, diabetes mellitus type 2 and coronary artery disease (4,5,6). C3b is the main effector molecule of the complement system, expressing multiple binding sites for other complement components such as C5, properdin, factor B, factor H and certain membrane proteins such as MCP). Binding these proteins to C3b leads either to amplification of C3 convertase, or initiation of Membrane Attack Complex (MAC). C3b also serves as an opsonizing agent to bind to the pathogen and target it for destruction by phagocytes. On the other hand, binding of C3b to complement component, factor I and a co-factor, inactivates C3b to iC3b and release C3f (2 kDa). iC3b can further be cleaved to form C3c, C3dg which further produces C3d and C3g (3). Overall, C3 promotes phagocytosis, supports local inflammatory responses against pathogens, and instructs the adaptive immune response to select the appropriate antigens for a humoral response (6). More recently, C3 has been suggested to have a pathophysiological role in Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative disorders (7). In clinical practice the level of (C3) in serum and CSF can be used to help identify immunological disorders, especially those associated with deficiencies of complement components.
HGNC name(s) : C3
Host : Mouse
Clonality : Monoclonal
ID : EnCor Biotechnology Complement component C3/C3 α-chain/anaphylatoxin 6B1
Reactivity : Hu specific
Isotype : IgM
Conjugation : none
Immunogen : Recombinant human C3 N-terminal anaphylatoxin construct
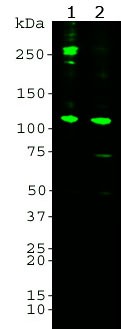
Mass of detected protein : 185 kDa pro-C3, intact α chain at 115kDa and lower molecular weight α chain fragments.
Uniprot ID : P01024
KGNC name : C3
RRID # : AB_2572254
Purification : Affinity purified at 1 mg/mL
Storage : Shipped on ice. Store at 4°C. For long term storage, leave frozen at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Validated applications : WB/ ELISA
Suggested Dilutions:
WB: 1:5 000-1:10 000.
References :
1. Janeway CA J, Travers P, Walport M et al. The complement system and innate immunity. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition (2001).
2. Brade V, Hall RE, and Colten HR. Biosynthesis of pro-C3, a precursor of the third component of complement. J. Exp. Med. 146:759-765 (1977).
3. Xia Z, Stanhope KL, Digitale E, Simion OM, Chen L, Havel P, Cianflone K. Acylation-stimulating Protein (ASP)/Complement C3adesArg Deficiency Results in Increased Energy Expenditure in Mice* J Biol Chem. 279:4051-7 (2004) .
4. Maslowska M, Vu H, Phelis S, Sniderman AD, Rhode BM, Blank D, Cianflone K. “Plasma acylation stimulating protein, adipsin and lipids in non-obese and obese populations”. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 29:679–86.(1999)
5. Koistinen HA, Vidal H, Karonen SL, Dusserre E, Vallier P, Koivisto VA, Ebeling P. Plasma Acylation Stimulating Protein Concentration and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue C3 mRNA Expression in Nondiabetic and Type 2 Diabetic Men”. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 21(6):1034–9 (2001).
6. Cianflone K, Zhang XJ, Genest J Jr, Sniderman A. Plasma acylation-stimulating protein in coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.17:1239-44 (1997).
7. Wang Y, Hancock AM, Bradner J, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, Jankovic J, Zabetian CP, Kim HM, Leverenz JB, Montine TJ, Ginghina C, Edwards KL, Snapinn KW, Goldstein DS, Shi M, Zhang J. Complement 3 and Factor H in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid in Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Multiple-System Atrophy. The American Journal of Pathology, Vol. 178:1509-16 (2011)
Additional information
| Format | 50 ul, 100 ul, 500 ul |
|---|---|
| Supplier | |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Conjugation | None |
Ask a question about Complement component C3/C3 α-chain/anaphylatoxin Antibody – MCA-6B1
You must be logged in to post a review.

Reviews