Encor Mouse monoclonal antibody to c-Fos
The c-Fos protein is a member of Fos family of transcription factors and is a cellular counterpart of the retroviral oncogene v-Fos. Other members of Fos family are FosB, Fra-1 and Fra-2. The Fos proteins associate with Jun proteins, but also with other basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domain proteins to create a variety of AP-1 (activator protein-1) complexes which bind to the promoters of numerous genes (1). Dimeric complex of these AP-1 transcription factors activate generally rapid physiological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, neoplastic transformation, apoptosis, and response to stress.
c-Fos and c-Jun are the best-studied AP-1 components and both contain bZIP motifs, necessary for binding to DNA and dimerization. c-Fos and c-Jun containing AP-1 dimers activate transcription in combination with coactivators, such as the CREB-binding protein and constituents of the basal transcription machinery, such as the TATA-binding protein (3, 4).
c-Fos is considered to be an immediate-early gene because expression is normally low but induced rapidly and transiently in response to a wide array of stimuli including serum, growth factors, tumor promoters, cytokines, and UV radiation. This allows cells to rapidly turn on specific genes to adapt to environmental changes. It plays an important role in many cellular functions, and is over-expressed in a variety of cancers.
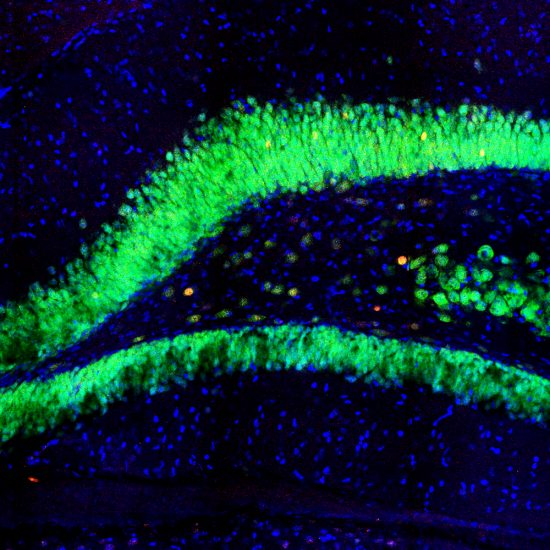
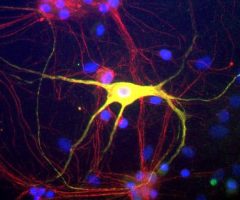
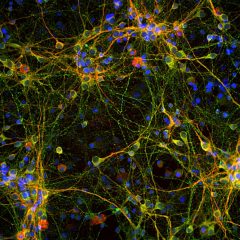
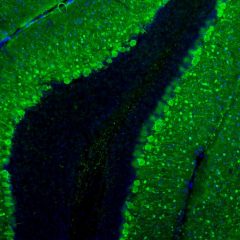
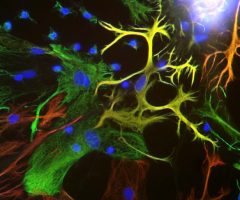
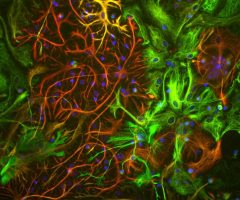
c-Fos is subjected to many different post translational modifications. Phosphorylation activates c-Fos, whereas sumoylation of c-Fos inhibits the AP-1 transcriptional activity (5, 6). Several lines of data demonstrate that expression of c-Fos in individual neurons can be used as a marker for neuronal activity, as there is an association between c-Fos expression and the firing of action potentials (7,8,9,10). Such work is usually done on histological sections of brain tissue and can be used to trace neuroanatomical connections, identify seizure pathways, and the sites of action of neuroactive drugs (8). Our MCA-2H2 antibody is proven to be an excellent reagent for these purposes.
MCA-2H2 was generated against full length human recombinant c-Fos protein expressed in and purified from E. coli. The HGNC name for this protein is FOS.
HGNC name(s) : FOS
Host : Mouse
Clonality : Monoclonal
ID : EnCor Biotechnology c-Fos 2H2
Reactivity : Human | Horse | Cow | Pig | Rat | Mouse
Isotype : IgG1
Conjugation : none
Immunogen : Recombinant full length human
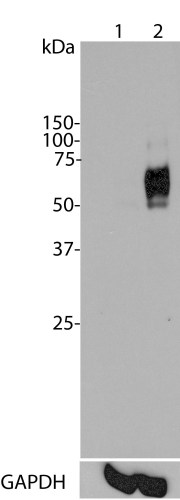
Mass of detected protein : 40.7 kDa (runs on SDS PAGE at 50-65 kDa)
Uniprot ID : P01100
KGNC name : FOS
RRID # : AB_2571561
Purification : Affinity purified at 1 mg/mL
Storage : Shipped on ice. Store at 4°C. For long term storage, leave frozen at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
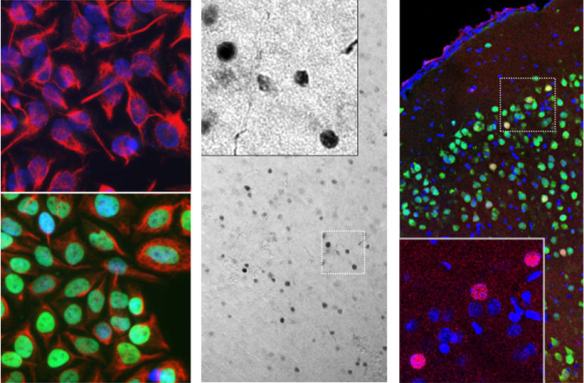
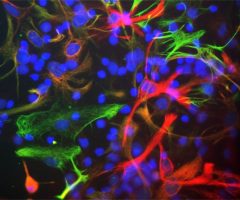
Validated applications : WB | IF/ICC | IHC
Suggested Dilutions:
WB: 1:1 000-2 000, ICC/IF or IHC: 1:1 000
References :
1. Mildle-Langosch K. The Fos family of transcription factors and their role in tumourigenesis. European Journal of Cancer 41:2449-2461 (2005)..
2. Chiu R, Boyle WJ, Meek J, Smeal T, Hunter T, Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell 54:541–52 (1988).
3. Bannister AJ and Kouzarides T. CBP-induced stimulation of c-Fos activity is abrogated by ElA. The EMBO Journal 14:4758-4762 (1995).
4. Metz R, Bannister AJ, Sutherland JA, Hagemeier C, O’Rourke EC, Cook A, Bravo R, Kouzarides T. c-Fos-induced activation of a TATA-box-containing promoter involves direct contact with TATA-box-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 14:6021-9 (1994).
5. Karin M. The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 270:16483-6 (1995).
6. Bossis G, Malnou CE, Farras R, Andermarcher E, Hipskind R, Rodriguez M, Schmidt D, Muller S, Jariel-Encontre I, Piechaczyk M. Down-regulation of c-Fos/c-Jun AP-1 dimer activity by sumoylation. Mol Cell Biol.25(16):6964-79 (2005).
7. Day HE, Kryskow EM, Nyhuis TJ, Herlihy L, Campeau S. Conditioned Fear Inhibits c-fos mRNA Expression in the Central Extended Amygdala. Brain Res.1229: 137–46 (2008).
8. Hoffman G, Smith MS, Verbalis JG. c-Fos and related immediate early gene products as markers of activity in neuroendocrine systems. Fronties in Neuroendocrinology 14:173-213 (1993).
9. Van Elzakker M, Fevurly RD, Breindel T, Spencer RL. Environmental novelty is associated with a selective increase in Fos expression in the output elements of the hippocampal formation and the perirhinal cortex. Learn. Mem. 15: 899–908 (2008).
10. Dragunow M, Faull R. The use of c-fos as a metabolic marker in neuronal pathway tracing. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 29:261–265 (1989).
Additional information
| Format | 50 ul, 100 ul, 500 ul |
|---|---|
| Supplier | |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Reactivity | Cow, Horse, Human, Mouse, Pig, Rat |
| Validated Applications | WB, IHC, IF/ICC |
| Conjugation | None |
| Isotype | IgG1 |

![RIGHT IF c-Fos Antibody - MCA-2H2 IF + R-GFAP[1] RIGHT IF c-Fos Antibody - MCA-2H2 IF + R-GFAP[1]](https://www.civicbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/cfos-2H2-R-GFAP-KCl1.jpg)
![LEFT IF c-Fos Antibody - MCA-2H2 IF + R-GFAP[1] LEFT IF c-Fos Antibody - MCA-2H2 IF + R-GFAP[1]](https://www.civicbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/cfos-2H2-R-GFAP1.jpg)
![RIGHT c-Fos Antibody - MCA-2H2 IF Chi-Vim--S[1] RIGHT c-Fos Antibody - MCA-2H2 IF Chi-Vim--S[1]](https://www.civicbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/cFos-2H2-Chi-Vim1.jpg)
![LEFT c-Fos Antibody - MCA-2H2 IF Chi-Vim--S[1] LEFT c-Fos Antibody - MCA-2H2 IF Chi-Vim--S[1]](https://www.civicbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/cFos-2H2-Chi-Vim-S1.jpg)
Reviews