High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase comparison
Using Unpurified gDNA Containing Polymerase InhibitorsHigh-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison on difficult genomic DNA samples.
Modern commercially available high-fidelity DNA Polymerases are derived from either Pfu and KOD. Pfu is an enzyme found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. KOD is an enzyme isolated from Thermococcus kodakaraensis. Both original enzymes have now been genetically engineered to offer better processing, lower mutation rates and faster extension rates. A modern trend in the market is to fuse the polymerases with a DNA binding domain such as the Sso7d DNA-binding domain in order to increase affinity for DNA and prevent the polymerase from ‘dropping-off’ the DNA template during DNA extension, thereby enhancing processivity and sometimes even fidelity. Such a fusion protein became very popular when Finnzymes commercialized the polymerase Phusion® (now owned by Thermo Fisher Scientific). Phusion® and Q5® DNA polymerases (the latter is a trademark of New England Biolabs) are considered as the most advanced polymerases on the market in 2016. A new generation of high-fidelity DNA polymerases is now emerging slowly. These are not fusion proteins, are very processive and do not require extreme PCR cycling conditions or even high primer concentrations such as in the case of Phusion and Q5 high-fidelity DNA polymerases. Hence, we perfromed a High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison using these novel DNA Polymerases.
For some templates or depending on the DNA extraction method, finding a high-fidelity enzyme (or even a regular Taq DNA polymerase) that can be versatile and perform under harsh conditions can be a challenge. For instance, Phusion® and Q5®’s recommended annealing temperatures for primers and DNA template can prove favorable in some instances but can also be problematic if the required annealing temperature exceeds that of the extension step during PCR cycling. High annealing temperatures, along with a 2-step PCR protocol (annealing and extension steps combined), augments the probabilitily of non-specific amplification. In such instances, there is no room for PCR optimization at all, but redesign the primers themselves. Phusion® and Q5® are said to obey to the Tm + 3 °C rule to determine the optimal annealing temperature (Ta) used in PCR cycling. In contrast, the general rule for Taq DNA Polymerase is Tm -5 °C.
The TransDirect® Animal Tissue PCR Kit uses a proprietary buffer in which samples are incubated for 10 min at room temperature and then heated 3 min at 95 °C. Lysates are then normally combined with 2x TransDirect PCR supermix containing a special inhibitor-resistant DNA polymerase (TransBD) and specific primers to perform PCR. The whole process is advantageous for high-throughput labs becuse it requires much less time and ressources (no centrifugation) and less pipetting steps than column-based gDNA extraction.The TransDirect Animal PCR kit was successfully used in another post (Direct PCR on hair, saliva, cheek scrub and dead skin lysates) to lyse cells from hair, saliva, cheek and dead skin.
Our goal was to perform a High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison under more difficult conditions. According the respectuve datasheets, TransStart FastPfu and TransStart FastPfu FLY, obey to the Tm -5 °C, rule with leading polymerases from competitors, namely Phusion® Hotstart II (M549; ThermoFisher Scientific) and Q5® high-fidelity DNA Polymerase (M0491; New England Biolabs) use Tm + 3 °C. Tests were carried on TransDirect® Animal Tissue kit lysates (performance described here) and on raw extracts of (unpurified) HeLa and 293 cell lysates.
Details
Date: updated February 4th, 2017
Type of experiment: PCR from human gDNA
DNA Polymerase: KKP*, TransStart FastPfu and TransStart FastPfu FLY
Competitors: Phusion® Hotstart II (M549; ThermoFisher Scientific) and Q5® high-fidelity DNA Polymerase (M0491; New England Biolabs)
*KKP is currently a prototype version of a new High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase currently under development.
Multiplex PCR setup, using KKP, FastPfu and FastPfu FLY, for human β-globin and MC2R amplification:
- H2O : fill to 20 ul
- 5x buffer : 4 ul
- dNTPs (2.5 mM): 1.6 ul (0.2 mM final)
- β-globin Forward primer (10 uM): 0.4 ul (0.2 uM final)
- β-globin Reverse primer (10 uM) : 0.4 ul (0.2 uM final)
- MC2R Forward primer (10 uM): 0.4 ul (0.2 uM final)
- MC2R Reverse primer (10 uM) : 0.4 ul (0.2 uM final)
- gDNA : 3 ul (various amounts; see gDNA gel)
- DNA Polymerase (2.5 u/ul) : 0.4 ul
Multiplex PCR setup, using Phusion and Q5, for human β-globin and MC2R amplification:
- H2O : fill to 20 ul
- 5x buffer : 4 ul
- dNTPs (2.5 mM): 1.6 ul (0.2 mM final)
- β-globin Forward primer (10 uM): 1 ul (0.5 uM final)
- β-globin Reverse primer (10 uM) : 1 ul (0.5 uM final)
- MC2R Forward primer (10 uM): 1 ul (0.5 uM final)
- MC2R Reverse primer (10 uM) : 1 ul (0.5 uM final)
- gDNA : 3 ul (various amounts; see gDNA gel)
- DNA Polymerase (2 u/ul) : 0.2 ul
Multiplex PCR cycling for High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison
Denaturation: 30s at 98 °C 35 x
- Denaturation: 10s at 98 °C
- Annealing: 20s at 58 °C (KP, KKP, FastPfu and FLY) or 60 °C (Phusion and Q6)
- Extension: 25s at 72 °C
Final extension: 240s at 72 °C
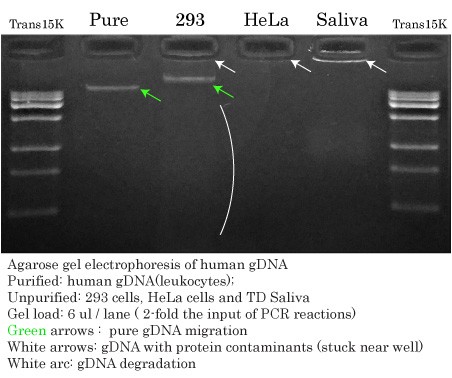
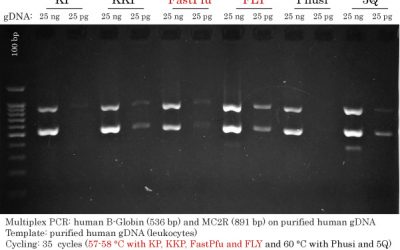
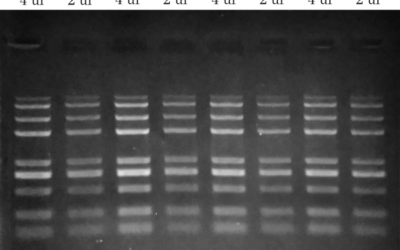
Input gDNAs used for High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparisons
The image shows the human genomic DNAs used in the following comparison of High-fidelity DNA Polymerases.
Two-fold volumes of gDNA (6 ul) (compared to PCR input (3 ul)) were run on an agarose gel to determine their migration pattern, relative concentrations and to reveal impurities and degradation.
- Pure genomic runs on an agarose gel between 20 and 40 kb (green arrows).
- Impurities such as proteins are present in the gDNA samples if the DNA gets ‘stuck’ near the bottom of the wells (white arrows).
- Degradation is normally seen as a smear all throughout the gel (white arc); DNA degradation is easier to see at the beginning of the migration.
- Relative gDNA concentrations were as follows: Pure ≈ 293 > TD Saliva >>> HeLa.
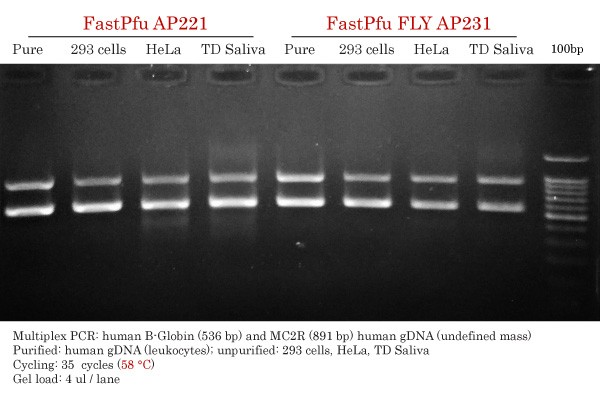
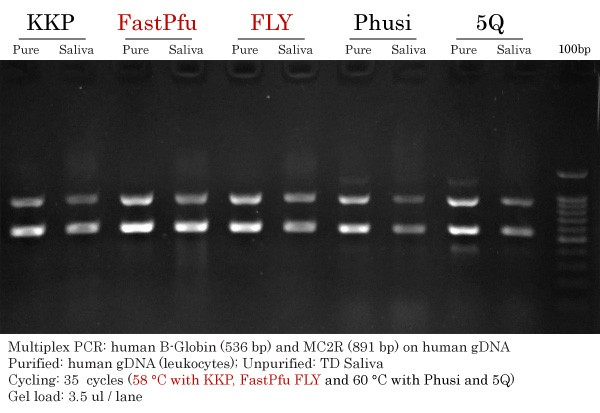
FastPfu vs FastPfu FLY High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison
PCR amplicons were obtained from purified or unpurified human gDNA samples, including TransDirect saliva samples using specific primers for human MC2R (891 bp) and ß-globin (536 bp). Primers were multiplexed together. An annealing temperature of 58 °C was used for both FastPfu and FastPfu FLY, despite the optimal being around 60 °C for FastPfu.
FastPfu :
- Specific with pure gDNA and 293 cells.
- Some smearing seen and faint non-specific diffuse band under the 536 bp band.
- Good intensity for both ß-globin (536 bp) and MC2R (891 bp).
FastPfu FLY :
- Specific with all input gDNAs.
- Good intensity for both ß-globin (536 bp) and MC2R (891 bp).
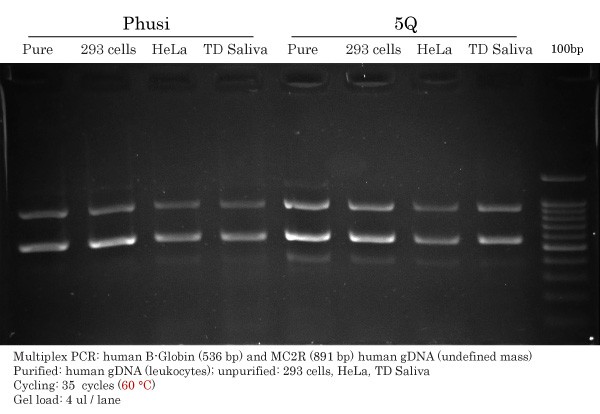
Phusion HS II vs Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison
Primers were multiplexed together. An annealing temperature of 60 °C was used for both Phusion and Q5.
Phusion :
- Appears specific with pure gDNA.
- Faint, yet present, non-specific band under the 536 bp band.
- Faint non-specific band above 891 bp, near 1250 bp. (see resume for a clearer view)
- Good intensity for both ß-globin (536 bp) and MC2R (891 bp).
Q5 :
- Faint non-specific band under the 536 bp band in all samples and also more intense than with Phusion.
- With pure gDNA, an additional non-specific band is seen above 891 bp, near 1250 bp.
- Good intensity, greater than Phusion, for both ß-globin (536 bp) and MC2R (891 bp).
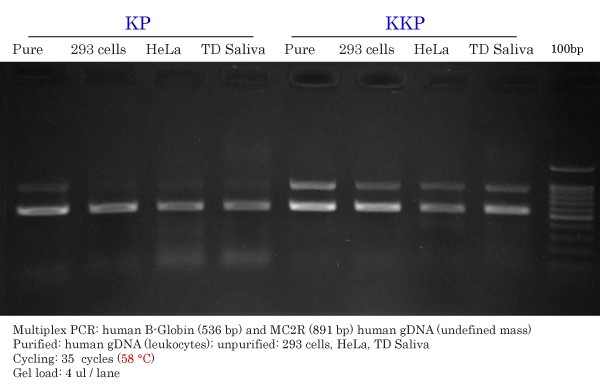
KP vs KKP High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison
Primers were multiplexed together. An annealing temperature of 58 °C was used for both KP and KKP.
KP :
- Specific with pure gDNA and 293 cells.
- Some smearing seen or faint non-specific diffuse band under the 536 bp band with HeLa and TD Saliva samples.
- Good intensity for both ß-globin (536 bp) in all samples but poor for MC2R (891 bp) in unpurified samples.
- A lot of primer ‘leftover’ at the bottom of the gel.
KKP :
- Nearly specific with all input gDNAs but similarly to FastPfu, a diffuse band is seen under the 536 bp band with HeLa and TD Saliva samples.
- Good intensity for both ß-globin (536 bp) and MC2R (891 bp) with all gDNAs.
Resume of High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison
Resume of PCR amplicons obtained in the High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase Comparison. Results for KKP, FastPfu, FastPfu FLY, Phusion and Q5 using purified human gDNA and TransDirect Saliva gDNA.
DNA Yield : FastPfu > FLY > Q5 > KKP = Phusion
Specificity : FLY > KKP > FastPfu > Phusion = Q5
Overall Performance : FLY > KKP = FastPfu > Q5 > Phusion
Which High-Fidelity DNA Plymerase would you choose?
According to these results, FastPfu FLY was the best overall performing High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase, providing high yield and absolute specificity in multiplex PCR regardless of the amount and/or purity of gDNA input. Notably, KKP, our a prototype enzyme, performed very well.
Want us to Compare your DNA Polymerase before you make the Switch?
DNA Polymerase Comparison Chart
Specifications and pricing of commercially available Taq DNA Polymerases and High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases in Canada.
Detection Limit of High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases on gDNA
Published on Jan 30, 2017 by Simon Roy, Ph.D Detection Limit of High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases using Human gDNA for Template We previously determined the detection limit of different Taq DNA Polymerases using human genomic DNA as a template for PCR. For this instance,...
PCR Purification Kit Comparison – DNA Clean Up
Which is the Best Kit for DNA Clean Up? Our aim was to perform a PCR Purification Kit Comparison from different vendors. At Civic Bioscience, we distribute the Favorprep™ and EasyPure® product lines from FAVORGEN and TransBionovo respectively. First, the FavorPrep™...